How Gastric Plication Helps With Weight Management?
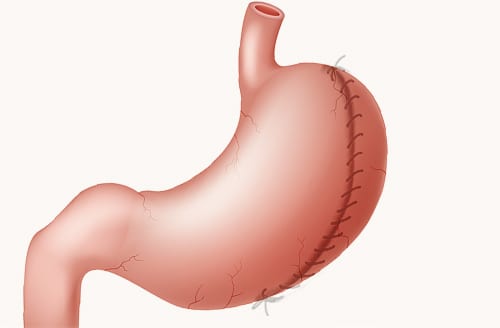
Gastric Plication is a minimally invasive bariatric procedure designed to reduce the size of the stomach by folding it inward. Unlike other surgical weight-loss procedures, this technique does not involve removing any part of the stomach or implanting foreign devices. The result is a smaller stomach pouch that limits food intake and promotes early satiety, helping individuals consume fewer calories. This procedure is gaining popularity, especially among patients who prefer a reversible and less invasive option. Gastric Plication in Dubai is increasingly becoming a sought-after weight-loss solution for those struggling with obesity and its associated health risks.
Why It’s Different From Other Weight Loss Surgeries
Unlike gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy, Gastric Plication maintains the stomach’s natural anatomy without cutting or stapling the stomach. This reduces the risk of complications and makes the recovery process shorter. Moreover, the procedure is reversible, which appeals to individuals who are unsure about permanent alterations to their digestive system.
How Gastric Plication Supports Long-Term Weight Management
Reduced Hunger and Early Fullness
One of the key benefits of Gastric Plication is the reduced capacity of the stomach. This anatomical change makes patients feel full after eating small amounts of food. As a result, they consume fewer calories throughout the day, contributing to gradual and sustained weight loss.
Promoting Lifestyle and Behavioral Changes
Gastric Plication not only alters the physical structure of the stomach but also acts as a behavioral reset. Patients are required to adapt to a healthier eating routine, including nutrient-dense meals and regular exercise. Over time, these changes become habitual, supporting long-term success beyond the initial weight loss phase.
Hormonal Regulation and Metabolic Boost
Although Gastric Plication does not directly alter hormone levels like some other procedures, the reduction in food intake can indirectly influence hunger-related hormones. When combined with physical activity and proper nutrition, the metabolic rate improves, aiding in sustained weight management.
Lower Risk of Complications
Because there is no stapling or re-routing of the intestines involved, the chances of leaks or malabsorption issues are significantly reduced. Patients can resume normal activities sooner and with fewer dietary restrictions during the recovery phase.
Suitable for a Broader Range of Candidates
Gastric Plication is often recommended for individuals who are not eligible or do not wish to undergo more invasive procedures. It is particularly effective for those with moderate obesity and those who have not had success with diet and exercise alone.
Who Can Benefit From Gastric Plication?
Ideal Candidates
This procedure is well-suited for individuals who:
-
Have a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 30 or above.
-
Have tried other non-surgical weight loss methods with limited success.
-
They are committed to long-term lifestyle changes.
-
Prefer a reversible and less invasive option.
Age and Health Considerations
Gastric Plication is generally considered safe for individuals between the ages of 18 and 65. A thorough preoperative assessment ensures that the patient does not have contraindications such as severe gastroesophageal reflux or certain chronic conditions.
Preventing Weight Regain
Maintaining a stable weight post-surgery requires consistent monitoring and support. Regular check-ins with nutritionists and behavior therapists can help reinforce healthy habits and prevent relapses.
Conclusion
Gastric Plication is emerging as a safe, effective, and less invasive alternative to traditional weight-loss surgeries. With its potential for reversibility and lower complication rates, it offers a promising path for individuals seeking long-term weight management without permanently altering their digestive system. By promoting satiety, encouraging healthier eating habits, and supporting lifestyle transformation, this procedure addresses the core challenges of obesity.



Comments
Post a Comment